Optimised management with IoT data
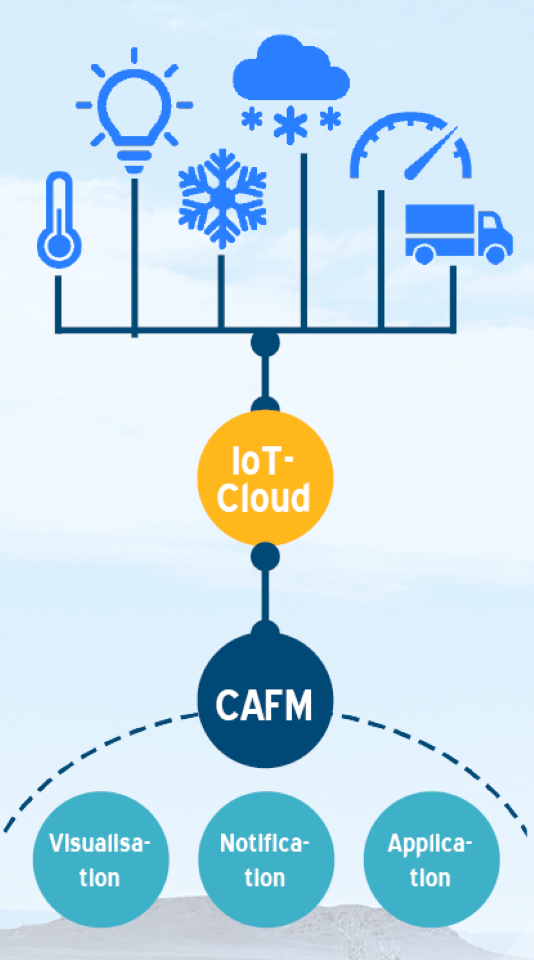
The interaction between the Internet of Things (IoT) and Computer Aided Facility Management (CAFM) has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of facility management. The networking of both technologies creates a powerful synergy in the management of buildings and facilities. Keßler Solutions and the self-service IoT platform akenza.io are joining forces to achieve this. Together, they are working to utilise resources more efficiently, reduce costs and improve the performance of buildings and facilities (e.g. by retrofitting them with sensors) by networking devices, automating processes and using real-time data.
Cooperation between Keßler Solutions and akenza
On 28 & 29 November 23, Keßler Solutions will be exhibiting with its IoT practice partner akenza at BIM world MUNICH (stand 33 in the foyer and congress lecture).
On 20.06.23, the two partners presented themselves together in a web event on the interaction of IoT and CAFM. This is published on Youtube, only in German.
For more information, please read the Announcement of the Web-Event with the topic “Powerful synergies: IoT in the interplay of management” (soon in German):
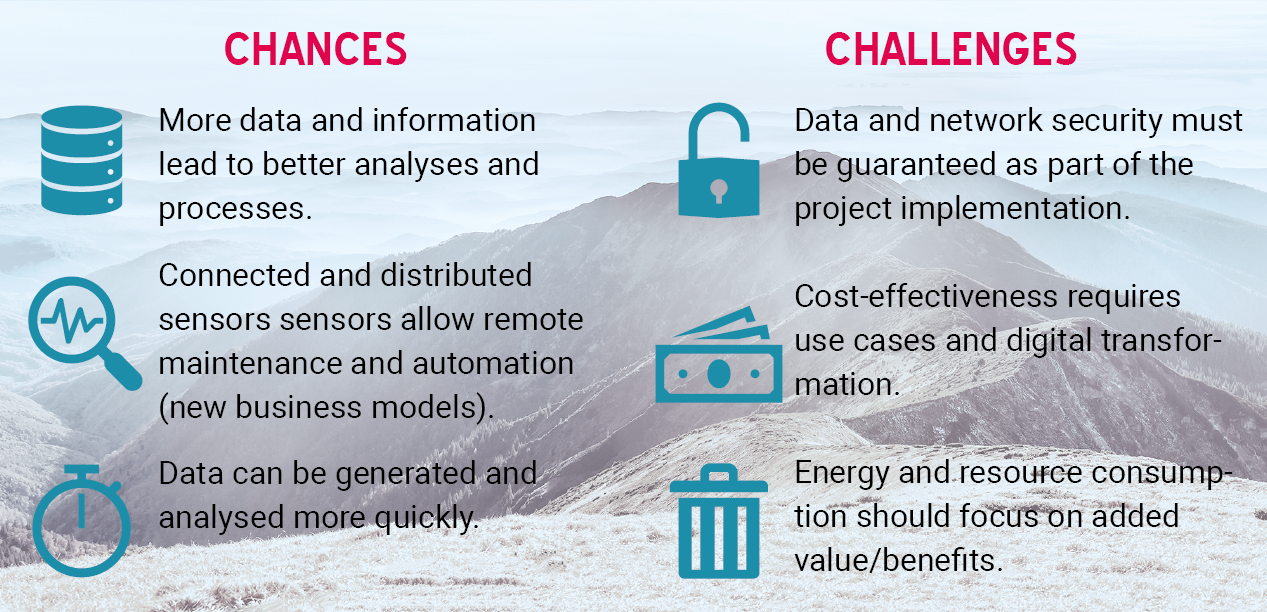
Opportunities and challenges of IoT in CAFM
If IoT-enabled sensors are installed in buildings, they can use real-time monitoring to recognise and report when limit values are exceeded and thus dangers, for example a fire via smart smoke detectors or a burst pipe via leakage sensors.
Resource consumption such as room temperature, air quality and/or lighting can be automatically monitored and thus regulated. Real-time monitoring of water and electricity consumption helps to reduce these and thus their costs and promote environmentally friendly practices.
Maintenance requirements can be identified at an early stage if the sensors provide data on the performance of machines and systems. Predictive maintenance measures can be planned sensibly to minimise downtime.
IoT devices are used to monitor building access and alarms, improving various aspects of security.
Intelligent sensors make it possible to analyse space utilisation. The condensed use of office space may lead to resource-optimised use of space and thus to cost savings.
By networking devices in a building, facility managers can organise their work more efficiently by strategically setting priorities based on current data and planning work routes and resources in a targeted manner. Examples include the cleaning department, whose workload is based on room utilisation, or the need for immediate action when a leak is reported.
The integration or connection of smart/intelligent sensors into the CAFM requires a robust IT-infrastructure and security precautions to ensure the integrity of the data and the privacy of the users.
Overall, IoT in CAFM/FM has the potential to help increase operational efficiency, conserve valuable resources, reduce costs, improve convenience for users and sustainably optimise practices. The Internet of Things is a central component of sustainable digitalisation.
Application examples from the IoT practice
The interplay between CAFM and IoT (Internet of Things) in operations is an important building block in the context of digitalisation and transformation processes. The collection of IoT data can be utilised in different ways. Below we present a small selection of possible use cases and processes.

Determination of faults
The focus is on detecting anomalies outside the standard range. This means, for example, that leakage sensors become active and report the ingress of water or the escape of chemical substances such as oil, petrol or gas. The sensor is triggered when a limit value is reached and the CAFM system automatically sends a fault message. This makes undetected leaks visible, for example in less frequented rooms, thus protecting property assets.
Determination of consumptions
The scenario is based on the continuous determination of consumption values for all types of utility meters. The CAFM system uses the regular consumption reports (e.g. for electricity, gas, hot or service water) to create utility bills, forecasts, evaluations and to visualise higher-level ESG criteria. Billing can be carried out according to various specifications and also directly at the metering point. The solution replaces complex metering lists and running lists in the inventory and reduces incorrect entries.

Recognise a-typical consumption
Negation of the standard or expected standard behaviour is reported here, e.g. consumption at unusual times. For example, if the CAFM system detects water being drawn from a school on a Saturday, it sounds an alarm. As this irregularity can indicate a leak and also unauthorised tapping, the FM or a stored responsible person, e.g. the head teacher, is automatically informed of the situation. It serves to prevent damage and unauthorised actions.
Smart services in property management
The management of property portfolios is subject to digital change. The provision of so-called “smart services” in operations offers great potential for additional sources of income in addition to rental income. Examples of this include charging points for electric cars, vehicle hire, bookable event rooms or offers for age-appropriate living. Future Living® Berlin is a lighthouse project with the involvement of Keßler Solutions.
![]()

Space and parking optimisation
The transformation of working environments towards modern and digital workplaces and spaces means that the utilisation and design of existing spaces must be rethought. Determining real space and resource requirements reduces costs in the long term. The FAMOS family offers the Workplace Management and Web App Events web apps for this purpose. Both products can be combined with IoT sensors and show, for example, current occupancy in the app and enable direct bookings.


